Ammonia An Acid Or Base
This blog post will talk over "is NH3 acid or base of operations? ". NHthree is as well known as Ammonia, and it is besides nowadays in the gaseous land. Ammonia is a very technical and complicated molecule to exist studied. This article will too acquire different theories that testify NH3 acid or base of operations. Some theories propose Ammonia'southward acidic and fundamental nature due to many factors like removal of or acceptance of proton H+ or OH–, ka and kb values, their dissociation abiding, and the presence of solitary pair.
Ammonia is a gas that has a pungent smell, is colorless, and is non-combustible gas. If y'all talk over its composition, information technology is made up of one nitrogen atom and three hydrogen atoms. Due to a very electronegative atom and dissimilar atoms N and H., information technology is Polar considering all-atom does non cancel out their effects and causes some of the dipole moment. According to the valence vanquish electron pair repulsion theory (VSEPR), its generic formula is AB3 type, and co-ordinate to hybridization, it possesses sp3 hybridization and Trigonal bipyramidal geometry. It has a bail angle of 107.five degrees due to the repulsion of lone pairs.
The actual angle of this geometry is 109.5 degrees. Ammonia can take strong hydrogen bonding betwixt nitrogen and hydrogen atoms, and so it can easily be liquefied. Ammonia is used equally an active ingredient in agricultural fertilizers and is an excellent nitrogen source in plants and animals. It is a highly toxic gas, and its exposure can cause harm to the lungs or even cause death. It possesses many industrial uses, i.e., refrigerant, disinfectant chemicals, and training of fertilizers.
Is NH3 Acid or Base of operations / Theories
Ammonia (NH3) is a highly complex compound to study because NH3 tin can act every bit a weak base of operations, an acid, and an amphoteric species. Different theories of acid, and base concept, i.due east., Arrhenius, Lowry-Bronsted, and Lewis's thought of acid and base of operations. In that location is an exception between all these concepts of acid and base of operations. Some ideas explain its acidic or bones nature in water or aqueous medium; some explain its nature on behalf of the presence of lonely pair. And some explanation on behalf of removal and acceptance of proton H+ ions.
NH3 is a weak base; nonetheless, its pH is xi and acts every bit an amphoteric species. Amphoteric species is the species that carry as an acid and the base. Its basicity value (pkb) is four.75, and information technology is miscible soluble in h2o. Three concepts of acid and bases will explain Ammonia's acidic or basic nature.
one. Arrhenius Concept of Acids and Bases
This concept is only valid for the dissociation that occurs in the aqueous medium. According to the definition of Arrhenius acid and base of operations:
- Acid is a substance that can donate a proton or H+ ion on dissociation in aqueous media, and the base is a substance that can donate OH- ions on the dissociation in the aqueous media.
- In other words, it is to be said that donation of H+ and OH- ions by an acrid or a base of operations cause increase in the concentration of H+ and OH- ions in the water.
According to the Arrhenius concept of acid and bases, NH3 acts equally an acid because it forms conjugate base of operations NH2+and the hydronium ion H3O+.
NH3 + HiiO → NH2+ + H3O
It is concluded by this reaction that information technology will not act as Arrhenius base of operations because the condition for Arrhenius base of operations is non satisfied. The requirement states that the Arrhenius base will donate OH- ions in the aqueous media. In the formula of Ammonia, there is no unit of measurement of Oh- ion, just like NaOH, KOH, etc. So, it will not act every bit Arrhenius Base.
2. Lowry-Bronsted concept of Acid and Base
Lowry and Bronsted proposed the concept of acid and base, and they did not explain this concept in aqueous media. According to the Lowry-Bronsted thought of acid and base:
- Acid is a substance that donates a proton to another species, but the base is a substance that accepts a proton from Lowry-Bronsted acid.
- Acid is a strong species if its conjugate base is stable, and the base is a stiff species only when its cohabit acrid is much more stable.
Consider the following reaction:
HCl + NH3 → NHiv+ + Cl–
In the reaction mentioned above, NH3 accepts a proton from HCl. So, according to the definition of this concept, NH3 acts as a base, and its conjugate acid is stable. So, this theory explains the basic nature of Ammonia NH3. It as well acts as an acid, called an amphoteric species. " Amphoteric species is the species that carry as an acid also every bit the base ."
3. Lewis Concept of Acid and Base
Lewis'southward concept was given by the The states scientist G. N Lewis in 1923, and he proposed this concept in his proper name. According to the idea of acrid and base of operations, Lewis acid and base can be divers equally:
- Lewis Acid is a substance that tin accept a pair of electrons from a donor and base is a substance that can donate a pair of electrons to an acceptor.
- Lewis Acid acts as an acceptor & lewis base acts as a donor. Lewis besides proposed a theory based on pair of electrons.
- It is besides ended that Lewis acid is a species that is electron deficient only Lewis base is the specie that is rich in a number of electrons.
Consider the following reaction betwixt Ammonia and boron trifluoride. In this reaction, NH3 acts as a Lewis Base because it donates the lone pair to the molecule of BF3 by a coordinate covalent bail. So, BF3 acts equally a Lewis acid due to the acceptance of the electron pairs. To prove the credence and donating of electron pairs on the newspaper we first have to make the Lewis structures of NH3 and BF3.
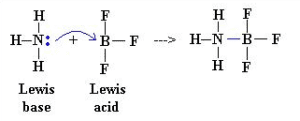
It is a neutralization process in which Lewis acrid and base react with each other to course an adduct species. Nitrogen attacks on the 2p – orbital of boron to form a coordinate covalent bond.
Stability according to conjugate acid-base pair
Conjugate acid is similar to the Lowry bronsted base which can take the proton and form when a Lowry bronsted acrid donates a proton. Just on the other hand, the conjugate base is similar to the Lowry bronsted acid which can donate a proton & form when a Lowry bronsted base accepts a proton. Information technology is to be noted that:
- A potent acid produces a weak cohabit base of operations.
- A strong base produces weak conjugate acrid.
- A weak acid produces a strong cohabit base.
- A weak base produces strong conjugate acid.
As in the following reaction, it is noticed that NH3 is a weak base because it accepts a proton from acid, so information technology forms the conjugate acrid. Then, a weak base forms potent conjugate acid which satisfies that it is a strong base. NH4+ is a strong cohabit acid so by this concept NH3 is a weak base.
NH3 + HtwoO → NH4+ + OH–
Properties of Ammonia
Ammonia possesses many of the following properties that are discussed below:
- Information technology has a molar mass of 17.031 chiliad/mol.
- The humid point of NH3 is -33.34 degrees and its melting point is -77.73 degrees.
- The dipole moment of NH3 is ane.42 D.
- Ammonia is lighter than air so can easily be liquified due to strong hydrogen bonding in nitrogen and hydrogen.
- The ammonia molecule undergoes nitrogen inversion at room temperature.
Uses of Ammonia
- Ammonia is used to manufacture many pharmaceutical products.
- It plays an important part in the agricultural field equally a fertilizer.
- Many other chemicals like plastics and dyes are manufactured by using Ammonia.
- For the purification of h2o supply and as refrigerant its role is not ignorable.
- In the fermentation process, information technology is used to modify the pH.
- Act as an antimicrobial agent and cleaning purposes.
- Also used to manufacture synthetic fiber similar nylon and thread.
- It is besides used equally the forerunner of the nitrogenous chemical compound.
Conclusion
It is concluded that according to Arrhenius NH3 acts as an acrid but other two concepts Lowry-bronsted and Lewis suggested that NH3 acts equally a weak base considering it possesses a potent conjugated acrid and a lone pair on it. As well, NH3 is discussed every bit a whole compound in this article.
Ammonia An Acid Or Base,
Source: https://www.uochemists.com/is-nh3-acid-or-base/
Posted by: stanfordsulthen01.blogspot.com



0 Response to "Ammonia An Acid Or Base"
Post a Comment